You can determine diabetes by paying attention to the symptoms that appear. With this endocrine disease, the health condition worsens. At first, many patients do not even pay attention to the first symptoms of diabetes mellitus, although with type I pathology they reduce the quality of human life in a few days. The later the disease is detected, the more difficult it is to achieve its compensation. Do not forget the signs of diabetes, this will allow you to consult a doctor at the right time if they occur.
Characteristics of the disease
Diabetes mellitus is a serious endocrine pathology in which there is an absolute or relative insufficiency of insulin. In the first case, it is not produced by the cells of the pancreas in the necessary quantities, and in the second case, it disrupts the process of the interaction of this hormone with the target cells.
Insulin is needed so that glucose entering the body can be absorbed by the tissues. If the hormone does not perform its functions, then sugar circulates in the blood for a long time. As a result, tissues and organs do not receive the necessary energy.

Pathology is manifested by the development of persistent hyperglycemia. The concentration of sugar is constantly above the norm. In this disease, all types of metabolism are disturbed. Problems arise from the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, water-salt, proteins and minerals.
Distribution
Endocrinologists distinguish the following types of diabetes:
- insulin dependent (type I);
- insulin independent (type II);
- gestational.
Type I diabetes is insulin dependent. This form of the disease is detected mainly in children and young people. The main symptoms in type I pathology are pronounced. In this form of the disease, insulin is not produced in the patient's body, so patients must inject this hormone every day.
In form II, the first signs do not appear immediately, they are mild. A person may not suspect that he has health problems for several years after the onset of the disease. Insulin is produced in the body, but the target cells become insensitive to it.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. After giving birth, the condition returns to normal, but a woman must be careful and follow a diet. Patients with this form are at risk of developing type 2 disease.
The first signs of diabetes
All symptoms of this endocrine pathology are divided into major and minor. Their appearance is characteristic of both forms of the disease. But insulin-dependent people mostly develop the main symptoms. They become pronounced during the period when no more than 20% of the cells responsible for insulin production remain in the pancreas.
Key features include the following:
- polyuria - increased urination, increased urine volume;
- polydipsia - the appearance of an obsessive thirst that cannot be quenched, the patient can drink more than 5 liters of water per day;
- polyphagia - increased hunger, after eating there is no feeling of satiety;
- weight loss - with the development of insulin dependence, people quickly lose weight.
In the first form of the disease, patients can even name approximately the date when they felt bad for the first time.
But the main symptoms also appear in type II of the disease. Their severity increases gradually. Therefore, often the patient cannot say when he felt changes in well-being for the first time. Patients independent of insulin notice the onset of minor symptoms earlier. But many of them can be confused with other diseases, so people do not immediately turn to an endocrinologist.

Secondary symptoms include the following:
- dry mouth;
- itching of the skin and mucous membranes;
- muscle weakness, increased fatigue;
- skin lesions that are difficult to treat;
- visual disturbances;
- constant headache;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- numbness of limbs.
But the main and secondary signs develop in all forms of pathology. It is possible to understand what type the patient suffers from without conducting a comprehensive examination on a specific basis. But for the specification of the diagnosis, the choice of treatment diagnosis is mandatory.
Type 1 symptoms
People whose cells responsible for producing insulin have been destroyed experience constant hunger. With an increase in the amount of absorbed food, their weight may decrease. Noticing such changes, it is necessary to immediately donate blood for sugar.
Other symptoms of insulin dependence include:
- increased nervous excitability;
- periods of vomiting without cause, nausea;
- the smell of acetone when breathing;
- pain in the region of the heart;
- sleep disturbance;
- sharp headaches.
The appearance of even 1 symptom should not be ignored. You can understand that there are problems by passing an analysis to determine the level of sugar in the blood. If you do not start insulin therapy when the first signs appear, then the patient's condition will deteriorate rapidly, he may fall into a diabetic coma.
Type 2 symptoms
Specific changes that may be suspected in the development of the non-insulin-dependent form of the disease include the following:
- pain in the limbs;
- cramps in the muscles of the legs, arms;
- weight gain;
- deterioration of sexual desire, problems with potency;
- decreased sensitivity to pain;
- weakening of the immune system;
- the appearance in the body of xanthomas - yellow formations that occur in violation of fat metabolism;
- growth of hair on the face while reducing their number on the legs.
But these manifestations in patients are often mild, so people do not pay attention to them. Many problems are discovered incidentally during a routine examination.
Features of the show
There are no significant differences in the development of the disease in men and women. It starts the same way in both sexes. They can differ only in minor symptoms.
The severity of pathological signs and the rate of development of the disease directly depends on the age of the person. Children and adolescents are diagnosed with type I diabetes. People over 40 develop type II disease.

Pathologies independent of insulin are detected more often in patients who:
- lead an inactive lifestyle;
- suffer from obesity;
- consume simple carbohydrates in large quantities;
- experiencing constant psycho-emotional stress.
You can distinguish the types of the disease from the symptoms.
To the children
Young people develop a predominantly insulin-dependent form of diabetes. This diagnosis is given to patients under 30 years of age. A doctor's consultation is necessary if a child or a young person has frequent urination, the volume of liquids they drink has increased significantly.
The possibility of developing the disease is higher in those children who:
- have a genetic predisposition to develop diabetes;
- born weighing 4. 5 kg;
- suffer from metabolic disorders (obesity, hypothyroidism);
- suffered a viral infection, as a result of which the cells of the pancreas could be damaged (rubella, measles, mumps and others).
With a mild form in children, adolescents, symptoms do not always occur, they can be almost invisible. Signs will appear only as the disease progresses.
In men
In adult patients, there is a risk of developing type 2 pathology. Men are prone to diabetes, in whom when they gain excess weight, first of all, the volume of the abdomen increases. With visceral obesity, the pressure on the internal organs increases, the work of the pancreas is interrupted.
Alarming symptoms are the weakening of sexual desire and impotence. A characteristic symptom can be inflammation of the foreskin - it occurs due to increased urination. The development of this condition contributes to the active reproduction of pathogenic bacteria.
Among women
One of the symptoms of diabetes is itching of the mucous membrane. Most often, women face its appearance - they have unpleasant sensations in the genital area. Most of them go to the gynecologist with the suspicion of infection with infections that are transmitted through sexual contact. If, according to the results of the tests, there are no sexually transmitted diseases, there are no problems with the microflora, then the doctor can advise the control of the sugar level.
Diagnosing
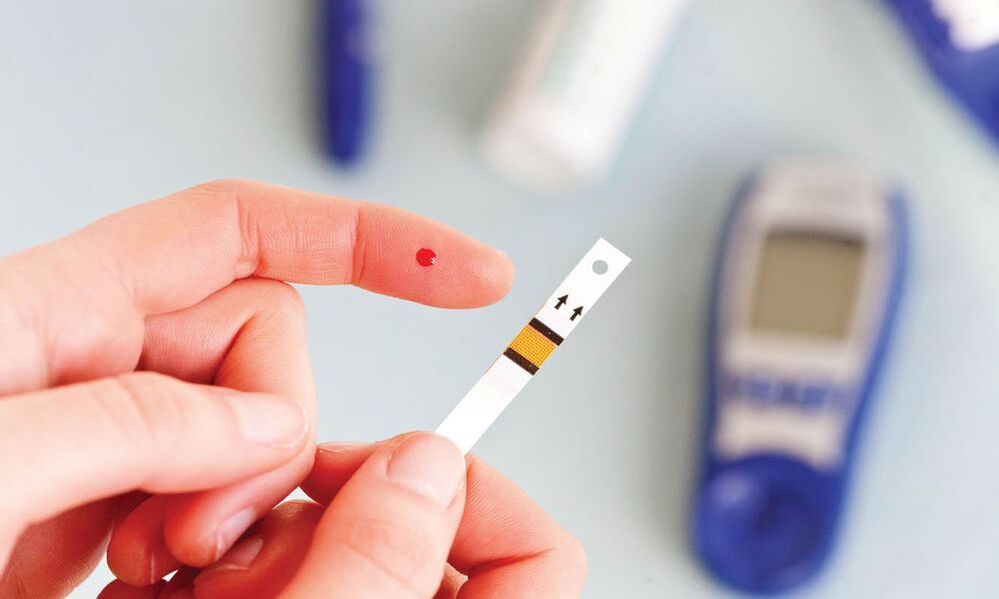
If symptoms of endocrine disorders appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Diabetes can be detected by tests that determine:
- the concentration of glucose in the blood on an empty stomach;
- glycated hemoglobin - shows the average level of sugar that the patient has had during the last 2-3 months;
- Glucose tolerance test - an analysis that is performed on an empty stomach and repeated after taking glucose.
The doctor can recommend donating blood at any time without prior preparation. This is necessary if there are characteristic signs of diabetes.
Which doctor to contact?
Patients who develop major, minor, or specific signs of diabetes should make an appointment with an endocrinologist. But a therapist can perform a preliminary diagnosis - he will give a direction for the necessary tests.
Based on the results of the examination, the endocrinologist can immediately give recommendations for nutrition, lifestyle changes and drug therapy. With a disease of the first type, insulin injections are necessary. Patients with type II diabetes are prescribed diet therapy, medications are selected, under the influence of which the target cells begin to more actively absorb insulin and glucose.